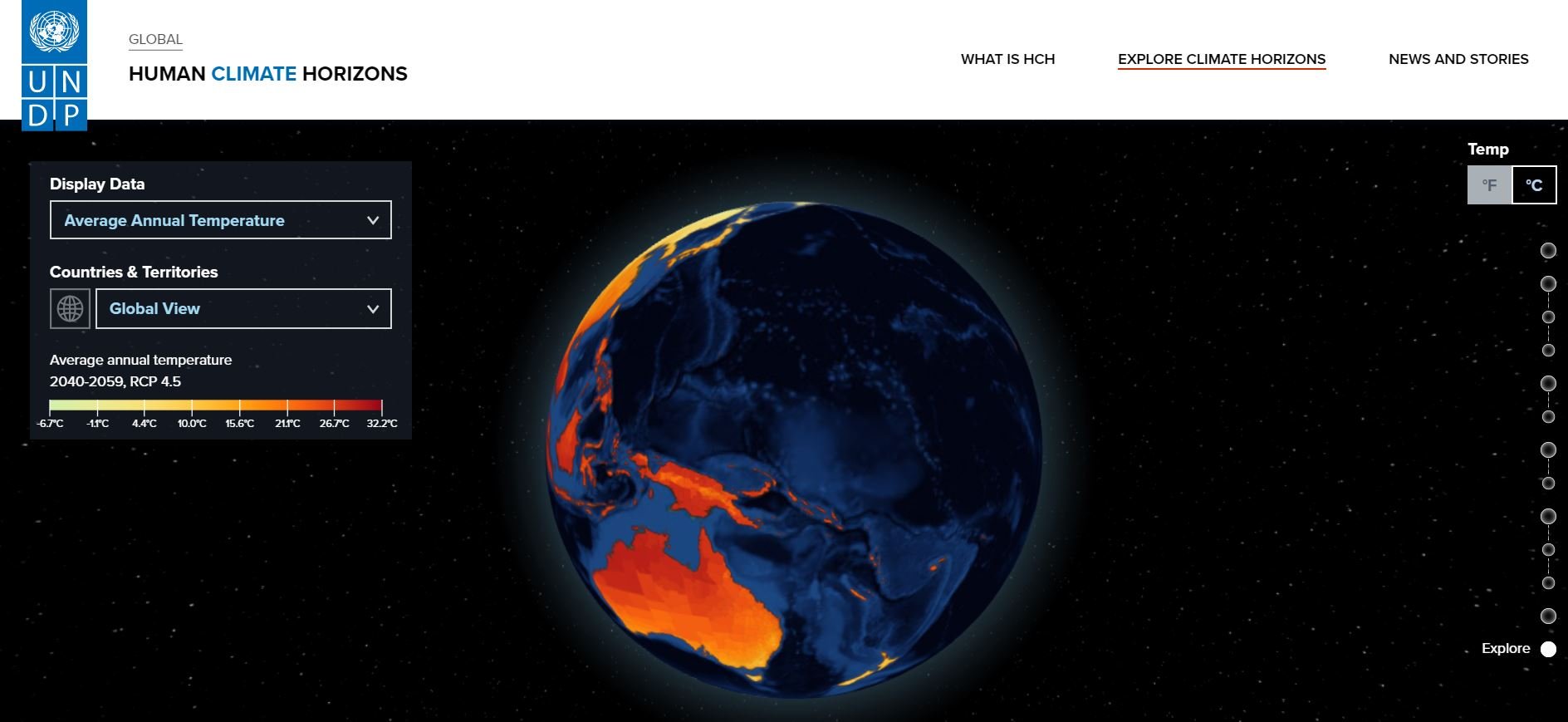
Jamaica is vulnerable to the impacts of climate change. In particular, it is likely to be affected by increased temperatures, changing precipitation patterns, sea level rise, and extreme weather events (especially hurricanes, flooding and drought). Both its natural resources and economic development are threatened by climate change (4). This has direct and indirect effects on human health, including economic insecurity, spread of vector-borne, waterborne and foodborne diseases, water and food insecurity, and death and injury from extreme weather events.
Through its 2015 Climate Change Policy Framework, Jamaica is working to mainstream climate change activities and help build capacity across sectors to develop adaptation and mitigation strategies (1). The government of Jamaica has also published its Nationally Determined Contribution (NDC). Human health is identified as a particularly important sector in Jamaica’s NDC, both in terms of adaptation and impacts. Indeed, human health is one of the main sectors listed as a priority for the development of climate change strategies and action plans (4). The NDC was further updated in July 2020 with more ambitious targets.